Vehicle-To-Grid (V2G) Overview & Working

What is Vehicle-To-Grid (V2G)?
Vehicle-to-grid, or V2G for short, is a technology that enables energy to be pushed back to the power grid from the battery of an electric vehicle (EV). With V2G technology, an EV battery can be discharged based on different signals - such as energy production or consumption nearby.
V2G technology powers bi-directional charging, which makes it possible to charge the EV battery and take the energy stored in the car's battery and push it back to the power grid. While bi-directional charging and V2G are often used synonymously, there is a slight difference between the two.
While bi-directional charging means two-way charging (charging and discharging), V2G technology only enables the flow of the energy from the car's battery back to the grid.

Components of Vehicle-To-Grid (V2G)
- Charge station
- Power converter(bidirectional)
- Transformer
- Main grid
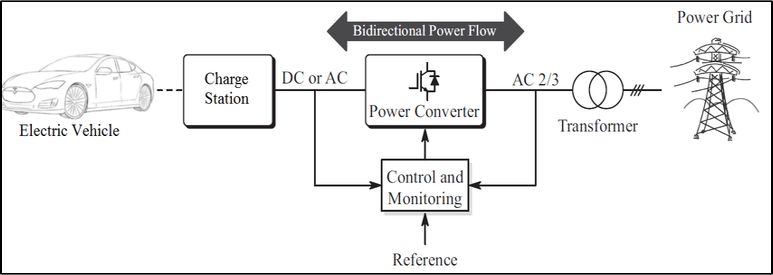
Working Principles of Vehicle-To-Grid (V2G)
The EV is plugged into a charge station, which is connected to a power converter, followed by a transformer connected to the main grid. A control and monitoring unit is present to provide accurate input to the converter by comparing the reference signal and the outputs of the power converter (because the converter is bidirectional, both its sides can be considered as the output side). Given that electric vehicles are integrated into electric energy, they are considered as an alternative energy source for the grid. Moreover, they are also used as uninterrupted power supplies (UPS). The vehicles consisting of V2G technology are generally charged at times when electricity production is higher, or at times when the price of electricity is low at peak load times, selling the energy to the grid at peak load times with high prices or when there is energy demand. In addition, this system also provides extra energy to the grid, increasing the reliability and efficiency of the energy system.
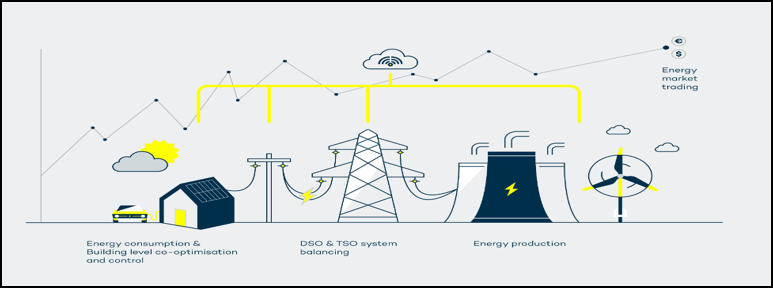
- Electricity at night is typically much cheaper than during the day due to considerably lower demand. Charging electric vehicles (EVs) overnight can save car owners a significant amount of money.
- Moreover, the reduced demand at night means that a larger proportion of the electricity used for charging comes from renewable sources, as opposed to fossil fuel power plants that may only be activated during peak times. This contributes to utilities' efforts to lower carbon emissions.
- In addition to assisting electricity suppliers in managing peak demands, the energy stored in EV batteries can also help them handle voltage and frequency fluctuations on the grid.
- Given the unpredictable nature of renewables, instances of cheap electricity may arise with little notice, such as unexpected windy weather. The V2G system, including any consumer-facing applications, must be flexible enough to respond promptly. EV batteries are well-suited to serve as a nearly instant source of power, available more quickly than activating other power generators.
The Benefits of Vehicle-To-Grid (V2G)
- Reduce total cost of ownership (TCO) of fleets
- Car OEMs (manufacturers) can sell vehicles with added value
- Energy market parties can trade and optimise their balance
- Network operators can optimise investments & stabilise the grid
About Effectual Services
Effectual Services is an award-winning Intellectual Property (IP) management advisory & consulting firm offering IP intelligence to Fortune 500 companies, law firms, research institutes and universities, and venture capital firms/PE firms, globally. Through research & intelligence we help our clients in taking critical business decisions backed with credible data sources, which in turn helps them achieve their organisational goals, foster innovation and achieve milestones within timelines while optimising costs.
We are one of the largest IP & business intelligence providers, globally serving clients for over a decade now. Our multidisciplinary teams of subject matter experts have deep knowledge of best practices across industries, are adept with benchmarking quality standards and use a combination of human and machine intellect to deliver quality projects. Having a global footprint in over 5 countries helps us to bridge boundaries and work seamlessly across multiple time zones, thus living to the core of our philosophy - Innovation is global, so are we !!!
Solutions Driving Innovation & Intelligence
Enabling Fortune 500's, R&D Giants, Law firms, Universities, Research institutes & SME's Around The Globe Gather Intelligence That
Protects and Nurtures Innovation Through a Team of 250+ Techno Legal Professionals.