Tech Coating to Cut Heat in Automotive Glass (Benefits & Key Technology Area)

Benefits of Coating Technology
Heat Rejection: Reflective coatings effectively reduce heat transmission through automotive glass, improving passenger comfort by minimizing heat buildup inside the vehicle.
Energy Efficiency: By lowering the need for air conditioning, these coatings contribute to reduced energy consumption, making the vehicle more environmentally friendly and economical to operate.
UV Protection: Many coatings block harmful ultraviolet (UV) radiation, preventing skin damage and protecting the interior of the vehicle from fading and wear.
Aesthetic Appeal: Reflective coatings can enhance the appearance of automotive glass, providing a sleek, modern look while maintaining clarity for drivers and passengers.
Privacy: Certain reflective coatings can reduce visibility from the outside without affecting the view from inside the vehicle, enhancing privacy for passengers.
Durability: High-quality coatings are resistant to scratches and environmental wear, ensuring long-lasting performance under various conditions.
Versatility: These coatings can be applied to different substrates, including glass, metal, and plastics, making them adaptable for various applications beyond automotive, such as in aerospace and architecture.
Factors Influencing Reflectivity of Coatings
Material Composition: Metals such as silver and aluminum are commonly used for their excellent reflectivity, while dielectric materials like TiO2 offer high reflectance when structured in thin, multilayered configurations.
Coating Thickness: Thicker coatings typically result in better reflectivity, but there is an optimal thickness for each material, beyond which additional thickness may not significantly improve performance.
Surface Smoothness: Smoother surfaces lead to higher reflectivity as they reduce light scattering. Ensuring a smooth substrate before applying the coating is crucial for optimal performance.
Angle of Incidence: Reflectivity tends to be highest when light strikes the coated surface perpendicularly. Coatings are typically optimized for a range of angles that vehicles encounter during daily use.
Wavelength of Light: Some coatings are designed to reflect specific wavelengths, such as infrared radiation, to prevent heat buildup while allowing visible light to pass through for better visibility.
Environmental Factors: Humidity, temperature changes, and exposure to pollutants can affect the performance of coatings, potentially degrading their reflectivity over time.
Glass Substrate Material: The glass substrate itself can affect how the coating behaves. Color, texture, and composition of the glass interact with the coating to determine the overall heat rejection capability.
Challenges of Coating Technology
Environmental Impact and Sustainability: The production and disposal of reflective coatings can have environmental implications, including energy consumption, waste generation, and potential toxicity. Sustainable manufacturing practices and recyclable materials are being explored to mitigate these concerns.
Maintenance and Durability: Over time, coatings may degrade due to exposure to environmental factors such as UV radiation, moisture, and pollutants. Regular maintenance and proper care are essential to ensure their longevity and effectiveness.
Cost-effectiveness: The initial cost of installing reflective coatings can be higher than traditional materials. However, these coatings' long-term energy savings and durability can offset the initial investment. Cost-benefit analyses are essential to assess the overall economic viability.
Application Challenges: Applying coatings to certain surfaces, especially curved or irregular shapes, can be challenging. Specialized techniques and equipment may be required for precise and uniform application.
Performance in Extreme Conditions: Reflective coatings must perform consistently under varying environmental conditions, including extreme temperatures, humidity, and chemical exposure. Ensuring durability and performance in such conditions is critical for their effectiveness.
Read Also: Tech Coatings to Cut Heat in Automotive Glass Overview and Types
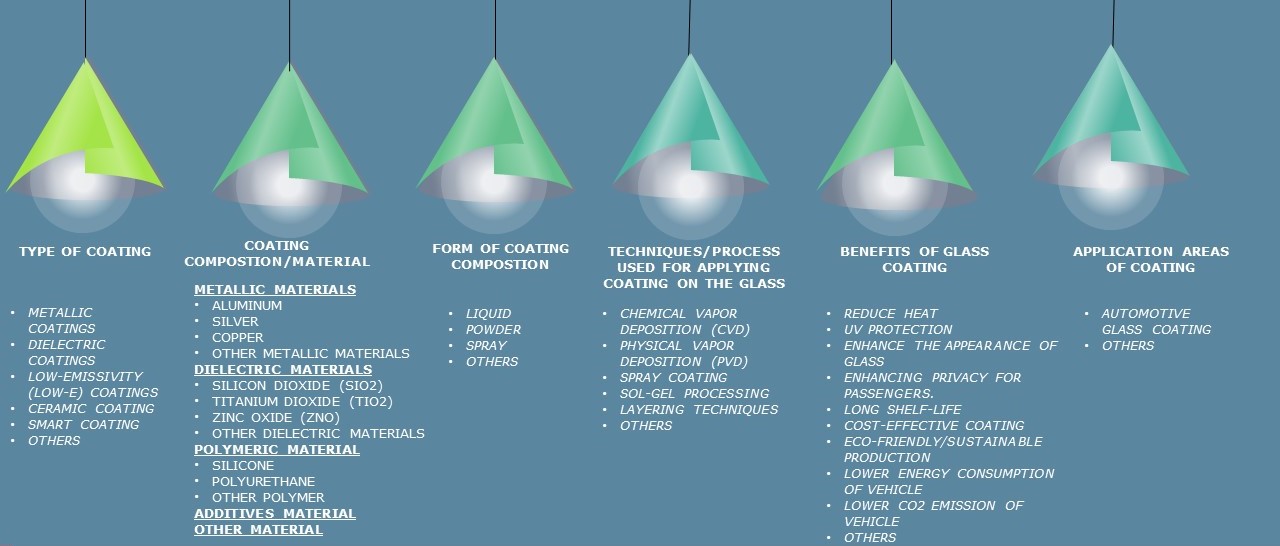
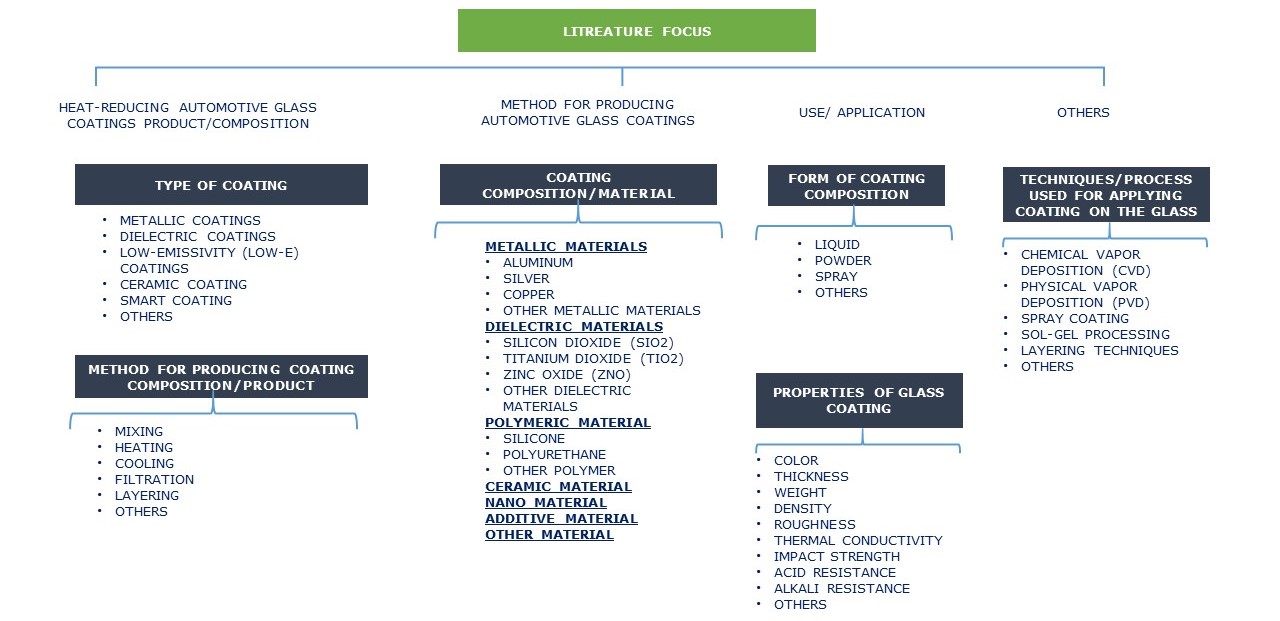
Key Technology Areas
Technology Cloud
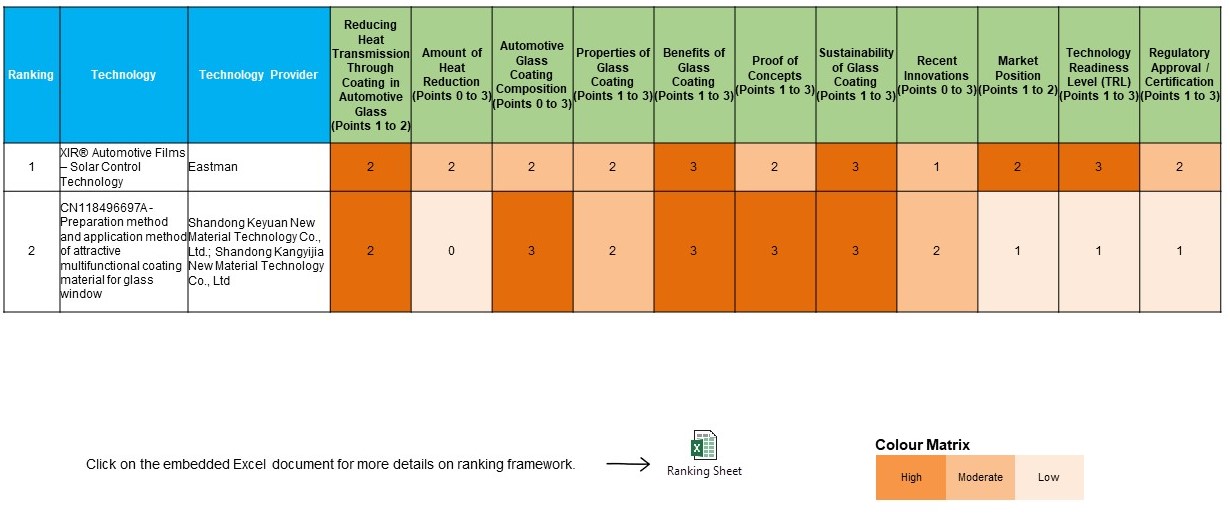
Ranking Framework
The below ranking framework is indicative. We may add more parameter depends on the project and client requirement.
REDUCING HEAT TRANSMISSION THROUGH COATING IN AUTOMOTIVE GLASS
- 2 points if the identified technology exactly discuss reducing heat transmission through coating in automotive glass with proof of concept.
- 1 point if the identified technology generally discuss reducing heat transmission through coating in automotive glass without proof of concept.
AMOUNT OF HEAT REDUCTION
- 3 points if the identified technology discusses more than 90% heat reduction through coating in automotive glass.
- 2 points if the identified technology discusses 50 to 89% heat reduction through coating in automotive glass.
- 1 point if the identified technology discusses 1 to 49% heat reduction through coating in automotive glass.
- 0 points if no information is available for the amount of heat reduction.
AUTOMOTIVE GLASS COATING COMPOSITION
- 3 points if the technology discusses completed details of the chemicals/materials used in the heat-reducing automotive glass coating, including their amounts/percentages.
- 2 points if the technology discusses the chemicals/materials used in the heat-reducing automotive glass coating, without their amounts/percentages information.
- 1 point if there is no information available for chemicals/materials used in the heat-reducing automotive glass coating.
PROPERTIES OF GLASS COATING
- 3 points if the identified technology discusses more than 3 properties of heat-reducing automotive glass coating.
- 2 points if the identified mineral processing technology 1-3 properties of heat-reducing automotive glass coating.
- 1 point if there is no information available for properties of heat-reducing automotive glass coating.
(Properties like color, thickness, density, roughness, thermal conductivity, impact strength, acid resistance, alkali resistance, etc.)
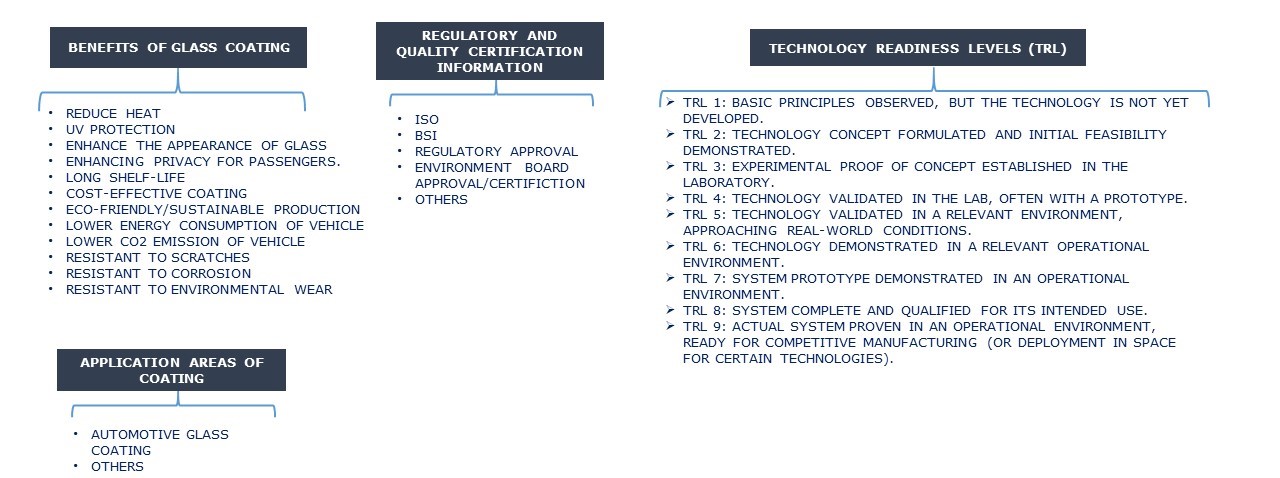
BENEFITS OF GLASS COATING
- 3 points if the identified technology discusses more than 3 benefits of heat-reducing automotive glass coating.
- 2 points if the identified mineral processing technology 1-3 benefits of heat-reducing automotive glass coating.
- 1 point if there is no information available for benefits of heat-reducing automotive glass coating.
(Benefits like reducing heat, UV protection, enhancing the appearance of glass, enhancing privacy for passengers, long shelf life, cost-effective coatings, eco-friendly/sustainable production, lower energy consumption in vehicles, lower co₂ emissions from vehicles, resistance to scratches, resistance to corrosion, and resistance to environmental wear, etc.)
PROOF OF CONCEPTS
- 3 points if the identified technology discusses proof of concept or test data for more than three benefits of heat-reducing automotive glass coating.
- 2 points if the identified technology discusses proof of concept or test data for one to three benefits of heat-reducing automotive glass coating.
- 1 point if the identified technology does not discuss proof of concept or test data for the benefits of heat-reducing automotive glass coating.
SUSTAINABILITY OF GLASS COATING
- 3 points if the identified technology for reducing heat transmission through automotive glass coating is sustainable or environmentally friendly.
- 2 points if the identified technology for reducing heat transmission through automotive glass coating does not discuss its sustainability information
- 1 point if the identified technology for reducing heat transmission through automotive glass coating is non-sustainable or adversely affects the environment.
RECENT INNOVATIONS
- 3 points if the identified technology has been developed in the last 5 years and is specifically mentioned as a novel or new technology.
- 2 points if the identified technology has been developed in the last 5 years.
- 1 point if the identified technology has been developed between 6 and 10 years ago.
- 0 point if the identified technology has been developed more than 10 years ago.
MARKET POSITION
- 2 points if the identified heat-reducing automotive glass coating technology is commercially available in a marketed product.
- 1 point if the identified heat-reducing automotive glass coating technology is not commercially available in a marketed product.
TECHNOLOGY READINESS LEVEL (TRL)
- 3 Points if the identified technology for reducing heat transmission through automotive glass coating exhibits a TRL level falling within the range of 7-9. (Deployment/commercialization).
- 2 Points if the identified technology for reducing heat transmission through automotive glass coating exhibits a TRL level falling within the range of 4-6 (Technology Development & Demonstration).
- 1 Point if the identified technology for reducing heat transmission through automotive glass coating exhibits a TRL level of 1-3 (Research Stage).
REGULATORY APPROVAL/CERTIFICATION
- 3 points if the technology for reducing heat transmission through automotive glass coating has quality certification and/or approval from regulatory authorities, and the information was obtained from the concerned regulatory body/organization's website.
- 2 points if the technology for reducing heat transmission through automotive glass coating has quality certification and/or approval from regulatory authorities, and the information was obtained from a third-party website.
- 1 point if no information is available regarding quality certification and regulatory approval.
Ranking Matrix
About Effectual Services
Effectual Services is an award-winning Intellectual Property (IP) management advisory & consulting firm offering IP intelligence to Fortune 500 companies, law firms, research institutes and universities, and venture capital firms/PE firms, globally. Through research & intelligence we help our clients in taking critical business decisions backed with credible data sources, which in turn helps them achieve their organisational goals, foster innovation and achieve milestones within timelines while optimising costs.
We are one of the largest IP & business intelligence providers, globally serving clients for over a decade now. Our multidisciplinary teams of subject matter experts have deep knowledge of best practices across industries, are adept with benchmarking quality standards and use a combination of human and machine intellect to deliver quality projects. Having a global footprint in over 5 countries helps us to bridge boundaries and work seamlessly across multiple time zones, thus living to the core of our philosophy - Innovation is global, so are we !!!
Solutions Driving Innovation & Intelligence
Enabling Fortune 500's, R&D Giants, Law firms, Universities, Research institutes & SME's Around The Globe Gather Intelligence That
Protects and Nurtures Innovation Through a Team of 250+ Techno Legal Professionals.