6G Technology: Future of Wireless Networks & Applications

Prelude
It's no secret that technology is developing at a breakneck pace. The speed of progress has been accelerated by developments in 3D printing, Blockchain, automation, robotics, machine learning, artificial intelligence, and wireless communication protocols like 4G and 5G.
Technological advancements have made it possible for businesses to improve their workflows and create innovative, game-changing goods and services. These developments enable innovative solutions based on consumer input and market demands. Customer happiness and the whole customer experience are greatly enhanced by this.
The fact that new technologies alter the way we communicate with one another and the outside world is arguably their most important contribution. With the most recent developments in technology, communication between people may happen more quickly.
Before, we had to wait days for snail mail letters to arrive at their destination. Email technologies nowadays enable instantaneous information transmission. Global connectedness is possible through wireless communications, including video conferences and instant messaging.
Since 4G has been there for a while, I believe it's reasonable to argue that we take advantage of its capabilities and assume the services we depend on will always function! We only check the top screens of our cellphones to determine if we have a strong enough signal when we experience a loss of service. When 5G is widely accessible, it will greatly enhance the technologies and services we already use, but it can only go so far in meeting our expectations and experiences. What happens when network communications change?
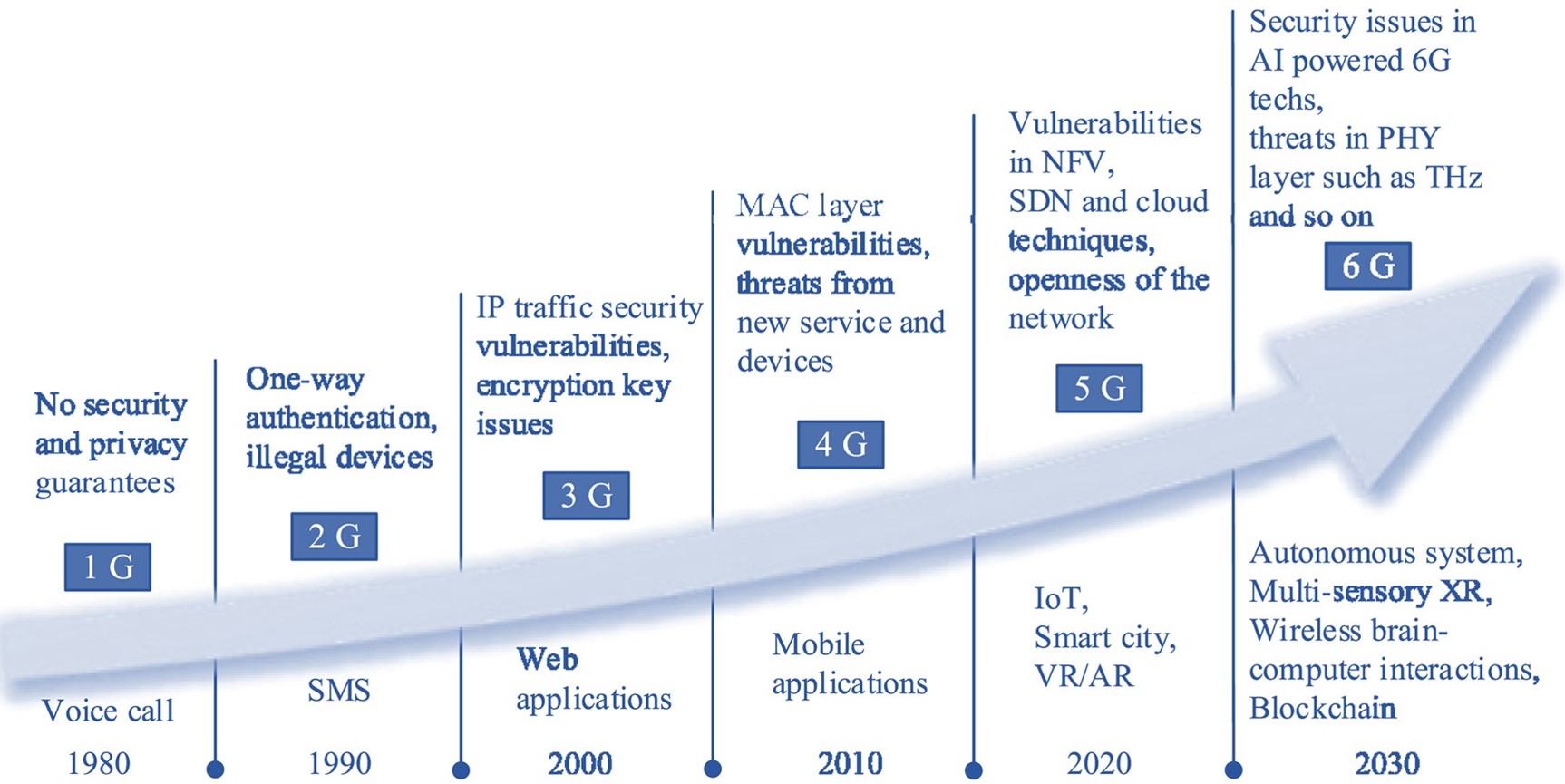
What precisely is 6G, then? Is it just a new name or a slogan used in marketing? No, is the response. Sixth generation (6G) technology, as its name suggests, is a wireless technology that will increase data transmission speeds and optimize our existing mobile network infrastructure. Higher bandwidth capacity and reduced latency are anticipated from the new technology, which will operate on a higher frequency spectrum than 5G.
Sixth-generation wireless networks, or 6G for short, are the advancements over 5G cellular technology. The majority of projections envisage the widespread implementation of 6G no earlier than 2030, however even that deadline is subject to disagreement. Similar to all preceding generations, 6G is anticipated to expand upon 5G's capabilities while incorporating advancements in digital technology. This will entail increasing data capacity and speed as well as implementing the IOT technologies that 5G is predicted to make feasible.
Amazing Speeds And Nearly Nonexistent Latency
In its most basic form, latency is the duration between a cause and an effect. For example, it controls the interval between sending a text message and the recipient receiving it. Every generation of wireless technology has concentrated on utilizing distinct portions of the spectrum, or the range of radio frequencies, to lower latency and provide greater connectivity, faster speeds, and innovative ways to amuse yourself with your smartphone.
With 4G, the typical delay is approximately 50 milliseconds. That is comparable to the speed of a lightning flash, yet it is still insufficient to handle extremely complex smart surroundings or gadgets.
The average latency of 5G is only one millisecond, which is five times faster than a hummingbird's wing flap. Because of its extremely low latency, the Internet of Things might eventually permeate daily life.
It is anticipated that 6G will give speeds 1,000 times faster than those of 5G. It will need to use radio frequencies that aren't presently congested with consumer electronics in order to live up to this expectation.
The frequency band from 95GHz to 3Thz, which has enormous data capacity and isn't currently being used for any commercial products, was opened in March 2019 by a unanimous vote of the FCC. Stated differently, moving large amounts of data in the same amount of time it takes light to travel 984 feet will become relatively simple.
Extreme Connectivity & Sensing
We will have more than merely quicker gadgets by utilizing the huge bands present at the lower terahertz and upper gigahertz frequencies. Our gadgets will be smarter and faster.
The majority of conjectures anticipate that 6G's extreme data rates and capacity will revolutionize connectivity overall, enabling us to link more devices at a rate that greatly above what 5G will be able to provide with smarter, more accurate data.
This extreme connectivity will allow for much more advanced data centers and "centimeter-level positioning" (as opposed to the feet-level precision with 4G) in its report on the applications of terahertz radiation. This directly affects robotic controllers, drone fleets, and monitoring equipment.
Comprehensive, Reliable Coverage
It anticipated that 6G would reach numerous milestones, one of which is "seven-nine reliability" (99.99999% reliability). That essentially means that coverage is available at all times and everywhere. The term "extreme coverage" refers to the creation of new borders in space, beneath the ocean, and on land.
The idea of expanding the internet into space is not new. Space firms have demonstrated themselves as significant investors in 5G networks, pointing out the network's ability to significantly expand coverage in locations like rural communities, where obtaining high-speed internet has sometimes proven to be unfeasible. That potential will grow with 6G; an internet of space things is even suggested in one study report.
Massive Advancements For Artificial Intelligence
According to some scientists, AI will eventually be able to analyze and transmit data at the same pace as a human brain because to 6G's speed and location accuracy. While 5G will increase the capabilities and accessibility of artificial intelligence, 6G is expected to revolutionize AI through "disruptive applications" that will significantly increase its visibility in our daily lives.
Unparalleled Energy Efficiency
The discussion surrounding 6G is distinct in that it incorporates concepts related to energy efficiency, which were not taken into account in earlier iterations of wireless networks.
According to one IEEE study, network infrastructure itself will be able to use energy harvesting technologies with 6G. With its enormous energy requirements, artificial intelligence will remain sustainable on the network with the support of such efforts.
NTT Docomo expands on this concept in its whitepaper. It anticipates that battery-powered electronics will become outdated with the arrival of the next wave of wireless technology. Radio signal-based power supply technology will take its place, resulting in ultra-low power consumption gadgets that are more energy-efficient.
How Will 6g Transform The World?
Commercial Uses
Contrary to 5G, which significantly expands on 4G users' capabilities, entertainment uses can be neglected in favor of 5G. The majority of research indicates that 6G will be widely used in the commercial sector since data-rich business environments are becoming more and more commonplace. Global brands, however, are already thinking about "immersive entertainment," which goes beyond virtual reality to produce an incredibly lifelike experience. A recurring theme in science fiction for a long time, we may now finally witness it.
Military & Security Purposes
6G has already attracted some interest and investment for military applications due to its potential for extremely precise positioning and extremely intelligent equipment. After implementing 5G last year, the Army is now investigating the potential applications of 6G in warfare.
Healthcare Applications
The healthcare technology industry is particularly interested in 6G since they see it as essential to creating broad, long-lasting smart monitoring. Smart healthcare will help the elderly population more effectively by monitoring blood pressure, diabetes, temperature, heartbeat, and more. It will also be better equipped to immediately notify the appropriate professionals when an emergency occurs.
What To Expect From Widespread 6G
What will happen when 6G is widely used, and what significant changes will we see at that point?
6G will, first and foremost, spark the metaverse. Despite being a popular term in the IT industry right now, even 5G can't provide the bandwidth required for real-time, personalized, rendered 3D environments. However, 6G will be able to provide that capacity and speed, allowing the big tech companies to build a persistent, fully integrated, and immersive virtual metaverse.
Furthermore, a greater variety of smart products will be available on the market thanks to 6G technology. There will be a significant increase in the number of internet-connected gadgets in our society that can gather and send data. The growing Internet of Things (IoT) combined with this pervasive intelligence will enable seamless internet communication between daily life and the internet.
Improving our online communication methods
We will meet in 3D virtual places where our avatars will make "real" eye contact, rather than wasting hours on 2D Zoom or Teams sessions. We will have the capability to convene in clusters and convey nonverbal cues instantaneously.
If a one-on-one meeting is required, we could easily swap out everyone and locate a peaceful virtual area to meet. Furthermore, you may "fly" or "teleport" to a digital twin and experience a product or factory directly from there.
Training The Workers Of The Future With VR And AR
Businesses will be able to offer engrossing VR and AR training experiences with 6G technology, which will expedite knowledge transfer between teams and improve retention.
The aerospace and engineering giant Honeywell is already enhancing its training initiatives with AR and VR. New hires are given mixed reality headsets by the corporation, which allow them to "see" the work that other employees are performing. The VR and AR technology overlays information to help the new hires learn while they imitate the duties.
Experiencing The New Social Media World
With 6G connectivity, we will utilize mixed reality glasses to view people's 3D worlds—rendering them in real-time and customizing them particularly for us—instead of accessing their 2D profiles on smartphones.
For instance, we might go to someone's virtual house and enjoy their artwork and vacation experiences recreated in three dimensions. Alternatively, we may arrange a virtual planet get-together for a fireside conversation with our new and old social media friends.
The Transformation Of Healthcare
The medical field will undergo a transformation thanks to 6G technology. We'll have smart sensors floating in our bloodstream, measuring and monitoring every facet of our health with lightning-fast data speeds.
These networked devices will gather data continuously, evaluate it, and provide recommendations and health issue predictions ahead of time. Additionally, smart technologies that can provide medical attention and physical support will be available to us. These devices will be backed by online digital avatars that are updated on a regular basis.
Our healthcare sector will transition from a reactive to a tailored and predictive model with the help of these new developments. This will significantly affect everyone who works in the healthcare industry now and completely change the way we take care of our health in the future.
Hitting the road with 6G
We will be able to handle the intense traffic in our future cities with the use of real-time, 4D maps made possible by 6G connectivity, which will also enable the use of autonomous vehicles both on the ground and in the air. Highly precise sensors in cars and base stations that can navigate and provide you with the fastest, most comfortable trip will make your commute better.
Will 6G Address 5g’s Shortcomings For The IOT?
It's difficult not to become excited about fantasy things like digital telepathy when one considers all the incredible technology that has been imagined and is fueled by genuine advancements in things like extended reality. These things might exist in the future, but it's unlikely that 5G will bring them about. Rather, we won't have ironed out all the bugs in the details—including some of the limitations that 5G currently presents—until 6G.
SECURITY -.We're still getting used to the idea that an object that doesn't seem like a computer may be connected to the internet and be hacked, and it's well known that the Internet of Things has serious security vulnerabilities due to the lack of standards. Researchers working on 6G are trying to solve this problem.
PRIVACY - What kind of privacy is there if everyone is wearing an implanted internet connection? (Researchers studying 6G haven't been able to respond either.)
COMPLEXITY - The enormous complexity of 5G already stems from the infrastructure that needs to be built out. Network reconfigurations for 6G might provide a solution, but there isn't one that works for now.
SOVEREIGNTY - One of the less talked-about issues surrounding 5G is whether there should be international standards or if national governments should be in charge of connectivity in their own territories. In the absence of a resolution to this dispute, the Internet of Things may be prevented from realizing its full potential.
Road to future
Although 5G implementation is still in its early phases, 6G research has already begun on the next generation of communication systems. Research and development (R&D) endeavors are underway in various locations with varied partners, and numerous commercial 6G initiatives have been launched globally. The number of patent applications for 6G and associated technologies is rising at an exponential rate. Numerous Standards Developing Organizations (SDOs) are working on 6G technology standardization, or at least have plans to work on it; some of the biggest tech companies have already begun trials and experimentation.
Governments and national research groups are contributing large sums of money to a number of projects.
Three new services—mobile holograms, digital replica, and immersive extended reality (XR)—that go beyond 5G capabilities are coming with 6G. The necessary data transmission rates exceed the 5G provided speeds, and the necessary hardware is now unavailable. It takes 0.9 Gbps throughput to stream a 16K UHD grade movie for virtual reality, and 580 Gbps to stream a hologram across a 6.7-inch screen. These are just two instances of the ultra-fast wireless connections that are only achievable with 6G.
The term "multi-sensory holographic teleportation" is even used to refer to the transfer of information across all senses, not simply three-dimensional images of distant things or people.
5G technology is at the center of a strong geopolitical and economic competition among numerous nations to establish global dominance. The likelihood of this tendency increasing with 6G is higher given that various nations want digital sovereignty, which is causing greater rivalry and divisions.
Starting to shape the sixth generation of mobile communication networks (6G) at a time when 5G is only now beginning to roll out globally may seem odd. However, future use cases like digital twins and teleportation, intelligent and autonomous transportation, and entirely digital commerce and payment experiences are already conceivable. I digress. Geopolitical issues have the potential to further fragment the world, not just in the field of mobile technology but also in many other areas. In fact, national academic and industrial researchers are being pressured by individual governments to produce as much intellectual property as they can in order to achieve digital sovereignty, which is influencing the 6G landscape.
It is critical to understand 6G patent dynamics and intellectual property protection in light of this trend. In this scenario, intellectual property rights are more than simply valuable assets; they are a defense mechanism to endure in a wide range of application industries utilizing a technology that is at the center of a bloody geopolitical conflict.
Innovation & Intellectual Property
In order to achieve the lofty 6G targets, new hardware and new materials must be developed. For thermal, optical, electrical, and electronic purposes, materials like graphene and metamaterials will be crucial, and llll-V compounds—which are expected to be highly helpful in 5G—will become even more crucial. Examples of novel hardware that is required are optical devices, software-programmable metasurfaces, and THz transistors, transceivers, diodes, and emitters. New kinds of fields include batteryless lithium-ion batteries that use nodal energy harvesting and wireless information and energy transfer (WIET) technology.
In light of current supply chain issues and geopolitical concerns, continents are looking for measures to bolster their strategic autonomy, notably in the area of technology. The field of chipsets and components for telecommunications devices is gaining a lot of attention from the political and industrial sectors.
The goal of the USA's CHIPS Act is to strengthen the country's chip supply chains, national security, and economy by fostering domestic semiconductor production and research and development. Comparably, by enhancing Europe's resilience and competitiveness in semiconductor applications and technologies, the European Chips Act seeks to reinforce Europe's position as a leader in technology. To assist in achieving the digital and green transformation, the EU has invested more than €43 billion. The European Leadership in Chips for 6G is the goal of the COREnect strategic roadmap, a Horizon 2020 initiative.
With the identification of over 9000 patent families pertaining to 6G enabling technologies, research and development efforts are surging. With a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of around 62% from 2015 to 2020, the technology growth trend is enormous and may be explained by the fact that the technology is still in its early stages of development, being in the Emerging stage of the Innovation Cycle.
Numerous stakeholders from the public and commercial sectors of academia and industry are already contributing to innovation and patent filings. The top 10 players control 19% of the ~9000 patent families. In addition to the engagement of the main telecom firms, IT companies like Intel, Samsung, and IBM are leading the research activities.
China is the primary 6G R&D hotspot, accounting for half of all 6G patent-related inventions. The USA and South Korea are the next two hotspots. Since 2015, the number of patent applications has increased, with the top three countries showing an exponential rise.
Blockchain/DLT, Energy harvesting, and Terahertz Communication are the top fields representing high research activities as potential technologies for 6G communication.
Please feel free to reach out to one of our subject matter experts at info@effectualservices.com
to explore, how we can help you & make the world a better place to live in !!!
Effectual’s 6G TECHNOLOGY RESEARCH FRAMEWORK is a deep dive into this ecosystem and shall help you understand the intricacies of this nascent innovative domain with insights backed with credible data sources. Some ways we can help include, but not limited to - Performing any previous art or freedom to operate searches to help you better grasp the environment surrounding your invention or business endeavors. If certain methods of IP protection are more appropriate for your technological or business goals, we can help you strategize effectively to plan for future & in making continuous innovation a part of your working model.
Solutions Driving Innovation & Intelligence
Enabling Fortune 500's, R&D Giants, Law firms, Universities, Research institutes & SME's Around The Globe Gather Intelligence That
Protects and Nurtures Innovation Through a Team of 250+ Techno Legal Professionals.